## Stock Car Brake Systems: A Comprehensive Overview (7,000 Characters)
### Introduction
In the world of high-performance motorsports, braking systems play a crucial role in maximizing vehicle speed and ensuring driver safety. Stock car brake systems are specifically designed to meet the demands of competitive racing, providing exceptional stopping power and durability. This article delves into the intricate details of stock car brake systems, exploring their components, functionality, and advancements.
### Components of a Stock Car Brake System
A stock car brake system primarily consists of the following components:
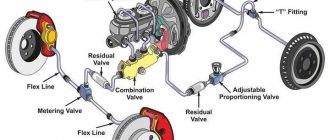
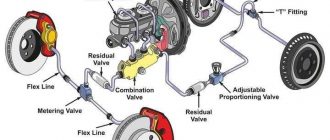
– **Master Cylinder:** Located in the engine compartment, the master cylinder pressurizes the brake fluid and distributes it to the wheels upon pedal application.
– **Brake Lines:** High-pressure metal or composite lines that carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers.
– **Brake Calipers:** Mounted on the wheel hubs, the calipers house the brake pads and apply pressure to them to create friction against the brake rotors.
– **Brake Rotors:** Discs attached to the wheels that rotate with them and are squeezed by the brake pads to generate stopping force.
– **Brake Pads:** Friction material that is pressed against the rotors to generate heat and slow down the rotation of the wheels.
### Functionality of a Stock Car Brake System
When the driver depresses the brake pedal, the master cylinder creates hydraulic pressure that is transferred through the brake lines to the calipers. The calipers receive this pressure and use it to activate the brake pads. The pads then clamp onto the brake rotors, creating friction that transforms the vehicle’s kinetic energy into heat. This heat is dissipated through the rotors and brake pads, causing the wheels to slow down and ultimately stop.
### Advancements in Stock Car Brake Technology
Over the years, stock car brake technology has undergone significant advancements to enhance performance and safety:
– **Ceramic Brake Rotors:** Ceramic rotors offer exceptional heat resistance and durability, reducing fade and extending lifespan.
– **Carbon Fiber Brake Pads:** Carbon fiber pads provide increased friction coefficient and heat tolerance, resulting in better stopping power.
– **Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS):** ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, maintaining vehicle stability.
– **Adjustable Brake Bias:** Allows drivers to fine-tune the front-to-rear brake force distribution, optimizing braking performance for different track conditions.
### Maintenance and Inspection
Proper maintenance and inspection of the brake system are paramount for ensuring optimal functionality and safety:
– **Regular Brake Fluid Changes:** Brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, reducing its effectiveness. Regular changes are crucial to maintain proper braking performance.
– **Brake Pad Replacement:** Brake pads wear out over time, requiring replacement. Worn pads can reduce stopping power and cause damage to rotors.
– **Rotor Inspection:** Check for cracks, warpage, or excessive wear. Replace rotors if necessary to ensure consistent braking performance.
– **Calipers and Lines Inspection:** Examine calipers for proper operation and check lines for leaks or corrosion.
### Conclusion
Stock car brake systems are highly engineered and specialized systems that play a vital role in the performance and safety of these high-speed racing machines. By understanding the intricacies of these systems, including their components, functionality, and advancements, we can appreciate the technology behind the intense braking maneuvers that characterize stock car racing. Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure optimal operation and the safety of drivers and spectators alike.