How Gas Car Engines Work
A gas car engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses gasoline as fuel. It is the most common type of engine in use today, and it can be found in a wide variety of vehicles, from cars and trucks to motorcycles and lawnmowers.
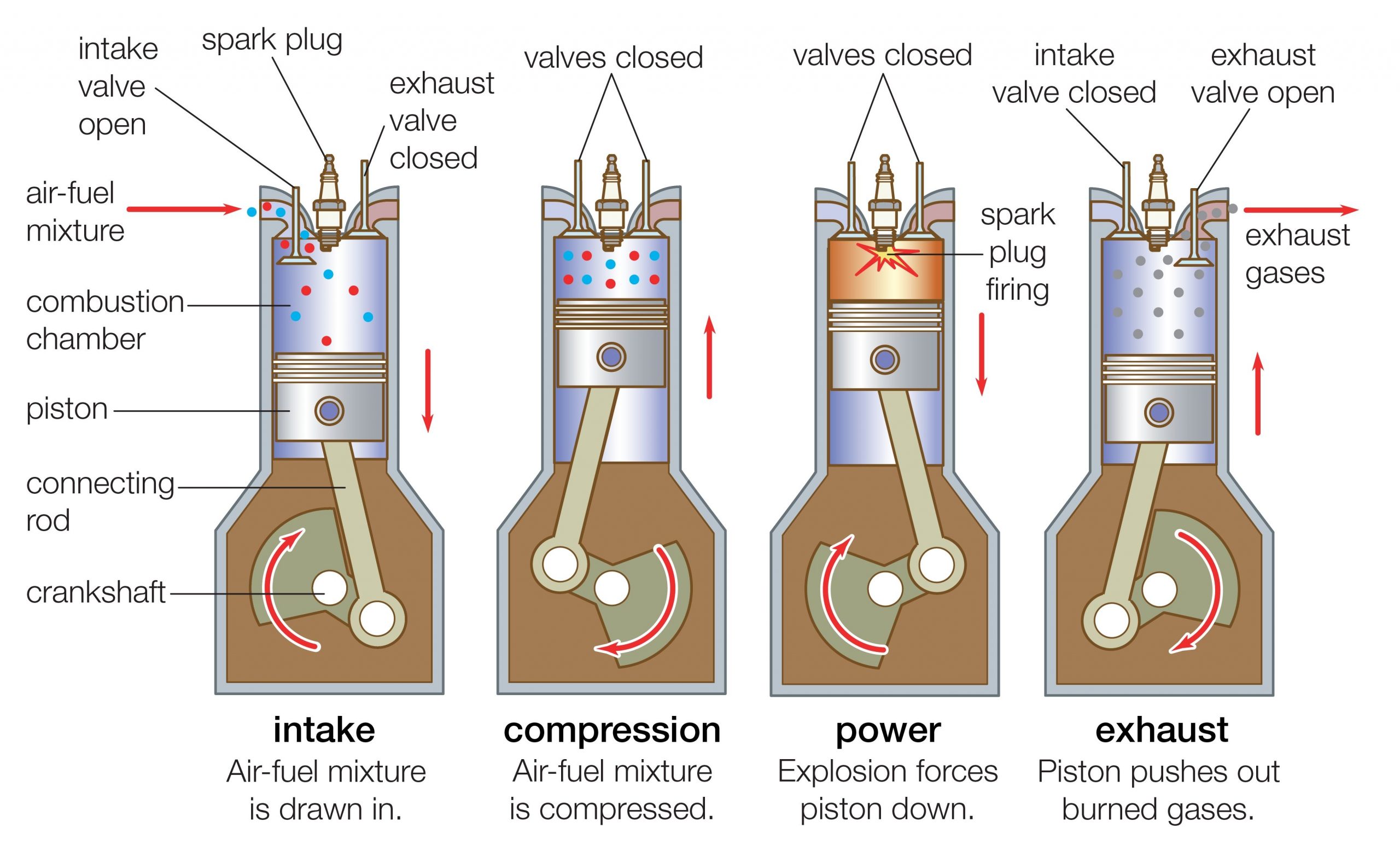
Gas car engines work by converting the chemical energy in gasoline into mechanical energy. This process begins when the gasoline is mixed with air and then ignited in the engine’s cylinders. The combustion of the gasoline creates hot gases that expand rapidly, driving the engine’s pistons. The pistons are connected to the crankshaft, which converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion. This rotary motion is then used to power the vehicle’s wheels.
The basic components of a gas car engine include:
— **Cylinders:** The cylinders are where the combustion of the gasoline takes place. They are typically made of cast iron or aluminum and are lined with a thin layer of steel to help protect them from the heat and friction of the combustion process.
— **Pistons:** The pistons are the moving parts that fit inside the cylinders. They are made of a lightweight metal, such as aluminum, and are designed to move up and down the cylinders as the gasoline combusts.
— **Crankshaft:** The crankshaft is the rotating part of the engine that converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion. It is made of a strong metal, such as steel, and is supported by bearings to help reduce friction.
— **Valves:** The valves are used to control the flow of air and gasoline into and out of the cylinders. They are typically made of steel or titanium and are opened and closed by the camshaft.
— **Camshaft:** The camshaft is the part of the engine that controls the opening and closing of the valves. It is made of a steel or aluminum alloy and is driven by the crankshaft.
The process of combustion in a gas car engine is a complex one. It involves the following steps:
1. **Intake stroke:** The intake valve opens, allowing air and gasoline to enter the cylinder.
2. **Compression stroke:** The piston moves up the cylinder, compressing the air and gasoline mixture.
3. **Power stroke:** The spark plug ignites the air and gasoline mixture, creating hot gases that expand rapidly. This expansion drives the piston down the cylinder.
4. **Exhaust stroke:** The exhaust valve opens, allowing the hot gases to escape from the cylinder.
The combustion process repeats itself over and over again, providing the power to drive the vehicle.
Types of Gas Car Engines
There are several different types of gas car engines, each with its own unique design and characteristics. Some of the most common types of gas car engines include:
— **Inline engines:** Inline engines have their cylinders arranged in a straight line. They are the most common type of gas car engine and are found in a wide variety of vehicles.
— **V-engines:** V-engines have their cylinders arranged in a V-shape. They are typically more compact than inline engines and are often used in high-performance vehicles.
— **Flat engines:** Flat engines have their cylinders arranged in a flat plane. They are the most compact type of gas car engine and are often used in sports cars and other low-profile vehicles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gas Car Engines
Gas car engines have a number of advantages over other types of engines, including:
— **High power density:** Gas car engines have a high power density, meaning that they can produce a lot of power for their size. This makes them ideal for use in vehicles that need a lot of power, such as cars, trucks, and motorcycles.
— **Low cost:** Gas car engines are relatively inexpensive to manufacture and maintain. This makes them a good choice for budget-minded consumers.
— **Widely available:** Gas car engines are widely available, making it easy to find parts and service.
However, gas car engines also have some disadvantages, including:
— **Low fuel efficiency:** Gas car engines are not as fuel-efficient as other types of engines, such as diesel engines. This means that they can use more fuel and produce more emissions.
— **High emissions:** Gas car engines produce a lot of emissions, including carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and climate change.
— **Noise:** Gas car engines can be noisy, especially when they are running at high speeds.
The Future of Gas Car Engines
Gas car engines have been the dominant type of engine in use for over a century. However, they are facing increasing competition from other types of engines, such as electric motors and hydrogen fuel cells. These newer technologies offer a number of advantages over gas car engines, including higher fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and quieter operation.
It is likely that gas car engines will continue to be used in vehicles for many years to come. However, it is also likely that they will gradually be replaced by other types of engines as these technologies become more mature and affordable.