##
- F1 Car Brake System – An In-Depth Analysis
- Introduction
- Components of the Brake System
- Brake Discs
- Brake Calipers
- Brake Pads
- Master Cylinder
- Brake Lines
- Hydraulic Fluid
- Design Considerations
- Cooling
- Weight Reduction
- Aerodynamics
- Performance Characteristics
- Deceleration Power
- Brake Pressure
- Brake Fade Resistance
- Safety Considerations
- Reliability
- Redundancy
- Conclusion
F1 Car Brake System – An In-Depth Analysis
###
Introduction
Formula 1 cars are renowned for their unparalleled speed and agility, but these feats would not be possible without their advanced braking systems. F1 car brake systems are engineering marvels that enable these vehicles to decelerate from blistering speeds in a matter of seconds, ensuring safety and control on the track.
###
Components of the Brake System
####
Brake Discs
F1 cars utilize carbon fiber brake discs that are significantly lighter and more durable than traditional steel discs. Carbon fiber’s high thermal conductivity allows it to dissipate heat rapidly, minimizing brake fade and ensuring consistent performance. The discs are typically 300 mm in diameter and are coated with a ceramic friction material for increased grip.
####
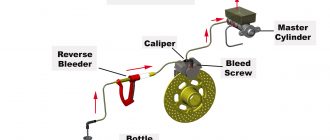
Brake Calipers
The brake calipers are responsible for applying pressure to the brake discs. In F1 cars, these calipers are typically made from titanium or aluminum to reduce weight. Multiple pistons (usually four to six) act on the brake pads, providing immense clamping force for effective braking.
####
Brake Pads
The brake pads are made from a high-friction ceramic composite material that provides excellent stopping power while withstanding extreme heat. These pads are designed to resist wear and tear, ensuring longevity even under the most demanding track conditions.
####
Master Cylinder
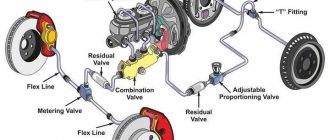
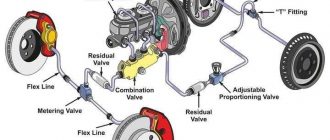
The master cylinder generates the hydraulic pressure that activates the brake calipers. It receives input from the driver’s brake pedal and converts it into sufficient pressure to engage the brake pads.
####
Brake Lines
Flexible brake lines connect the master cylinder to the brake calipers. These lines are made from braided stainless steel and are designed to withstand the immense pressures generated during braking.
####
Hydraulic Fluid
The hydraulic fluid used in F1 brake systems is a high-performance, heat-resistant fluid. This fluid transmits the pressure from the master cylinder to the calipers and helps lubricate the system’s moving parts.
###
Design Considerations
####
Cooling
The intense heat generated during braking necessitates effective cooling systems. F1 cars employ various methods to cool the brake system, including:
* **Cooling Ducts:** Air ducts direct cool air to the brake discs and calipers, dissipating heat and preventing overheating.
* **Brake Ventilation:** Holes drilled into the brake discs promote airflow and assist in heat dissipation.
####
Weight Reduction
Every gram counts in F1, and the brake system is no exception. Designers strive to reduce weight by using lightweight materials, such as titanium, aluminum, and carbon fiber.
####
Aerodynamics
The shape and position of the brake system can also affect the car’s aerodynamics. By designing the brake components strategically, engineers can improve airflow over the car, reducing drag and maximizing performance.
###
Performance Characteristics
####
Deceleration Power
F1 car brake systems are capable of generating immense deceleration forces. These cars can decelerate from 200 km/h (124 mph) to 0 km/h (0 mph) in just 70 meters (230 feet).
####
Brake Pressure
The brake pressure in F1 cars can reach up to 100 bar (1,450 psi). This immense pressure provides the necessary force to clamp the brake pads firmly onto the discs, generating the required frictional force for deceleration.
####
Brake Fade Resistance
Brake fade refers to the loss of braking performance due to excessive heat. The carbon fiber brake discs and ceramic pads used in F1 cars exhibit excellent brake fade resistance, ensuring consistent stopping power even under extreme track conditions.
###
Safety Considerations
####
Reliability
The reliability of the brake system is paramount for driver safety. F1 teams employ thorough testing and maintenance protocols to ensure that the brake system performs flawlessly in all racing conditions.
####
Redundancy
As an additional safety measure, F1 cars often have redundant brake systems. In the event of a primary brake system failure, the secondary system can be engaged to maintain control of the vehicle.
###
Conclusion
The F1 car brake system is a technological marvel that plays a crucial role in the safety, performance, and control of these high-performance machines. From the advanced materials used to the intricate design, every aspect of the brake system is meticulously engineered to deliver exceptional deceleration capabilities, enabling drivers to push the limits on the track with confidence.