**
Emergency Brake System in Car
**
**
Introduction
**
An emergency brake system, also known as a parking brake or handbrake, is a crucial safety feature in cars. It is designed to provide an independent braking mechanism in case the primary brake system fails or becomes less effective. This secondary braking system helps prevent the vehicle from rolling away when parked on a slope or in an emergency situation.
**
Types of Emergency Brake Systems
**
There are two main types of emergency brake systems used in cars:
**1. Mechanical Emergency Brake:**
* This type of emergency brake uses a mechanical cable or linkage to activate the rear brakes.
* When the lever or pedal is engaged, the cable pulls the brake pads against the brake disc or drum, slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
**2. Electronic Emergency Brake (EPB):**
* EPBs are more modern and use an electronic control unit (ECU) to activate the brakes.
* When the EPB button is pressed or the lever is pulled, the ECU sends a signal to electric motors that engage the brake pads.
* EPBs often include additional features such as hill-hold assist and automatic brake hold.
**
Parts of an Emergency Brake System
**
**1. Emergency Brake Lever or Pedal:**
* This is the primary control for the emergency brake system.
* In mechanical systems, it is typically a lever located between the driver’s seat and center console. In EPBs, it is usually a button or switch on the dashboard or center console.
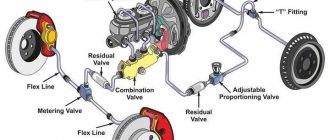
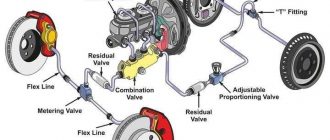
**2. Brake Cables or Actuators:**
* These components transmit the force from the emergency brake lever or pedal to the rear brakes.
* In mechanical systems, they are flexible steel cables. In EPBs, they are electric actuators.
**3. Rear Brake Calipers:**
* These are the brake components that apply pressure to the brake pads.
* In most cars, the emergency brake actuates the rear brakes only.
**4. Brake Pads:**
* The brake pads are friction materials that create the necessary force to slow down or stop the vehicle.
* Emergency brake systems typically use separate brake pads from the primary brake system.
**5. Rotor or Drum:**
* These are the rotating components that the brake pads come into contact with to create friction.
* In disc brakes, it is a rotor. In drum brakes, it is a drum.
**
How an Emergency Brake System Works
**
**1. Mechanical Emergency Brake:**
* When the emergency brake lever is pulled, it activates the brake cables, which pull on the rear brake calipers.
* The calipers then squeeze the brake pads against the rotor, slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
**2. Electronic Emergency Brake (EPB):**
* When the EPB button is pressed or the lever is pulled, the ECU sends a signal to the electric actuators.
* The actuators then engage the brake pads with the rotor, slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
**
Advantages of Emergency Brake Systems
**
* **Backup Braking System:** Provides a second line of defense in case the primary brake system fails.
* **Parking Brake:** Keeps the vehicle from rolling away when parked on a slope.
* **Emergency Stopping:** Can be used in conjunction with the primary brake system to quickly bring the vehicle to a stop in an emergency.
* **Hill-Hold Assist:** Prevents the vehicle from rolling backward when starting on an incline (in EPBs).
* **Automatic Brake Hold:** Holds the brakes engaged until the accelerator pedal is pressed (in EPBs).
**
Maintenance and Care
**
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the emergency brake system. Regular inspections and adjustments may be necessary, especially for mechanical systems. Some common maintenance tasks include:
* Inspecting the brake cables or actuators for damage or corrosion
* Lubricating the brake cables
* Adjusting the brake pads as they wear
* Replacing the brake pads when necessary
**
Conclusion
**
An emergency brake system is an essential safety feature in cars, providing an independent braking mechanism in case of primary brake system failure or for parking on slopes. Understanding how it works and properly maintaining it is crucial for the safety and well-being of both the driver and passengers.