What Cars Came with Rotary Engines?
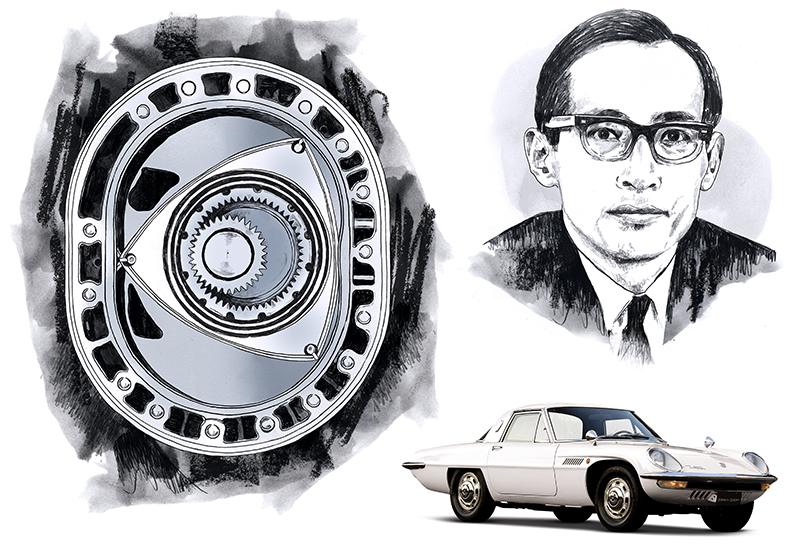
Rotary engines, invented by Felix Wankel, are a type of internal combustion engine that uses a triangular rotor that spins within a figure-8 shaped chamber to create power. They offer several advantages over traditional piston engines, such as being smoother and more compact. However, they also have some drawbacks, such as being less fuel-efficient and more prone to wear and tear.
Mazda
Mazda is the only automaker to have mass-produced cars with rotary engines. They first introduced the rotary engine in the Cosmo Sport 110S in 1967, and continued to use it in various models until 2012. Some of the most notable Mazda rotary-powered cars include:
- Mazda Cosmo Sport 110S
- Mazda RX-2
- Mazda RX-3
- Mazda RX-4
- Mazda RX-5
- Mazda RX-7
- Mazda RX-8
Other Manufacturers
A few other manufacturers have also experimented with rotary engines, but none have produced them on a large scale. These include:
- NSU (Germany): Ro 80
- Citroën (France): GS Birotor
- Wankel (Germany): Spider
- Norton (UK): Interpol 2
Advantages of Rotary Engines
- Smoothness: Rotary engines have no reciprocating parts, which makes them much smoother than piston engines. This can be a significant advantage in sports cars and other high-performance vehicles.
- Compactness: Rotary engines are much more compact than piston engines, which gives them a weight advantage. This can be important in small vehicles and aircraft.
- Power-to-weight ratio: Rotary engines have a very high power-to-weight ratio, which means they can produce a lot of power for their size. This makes them ideal for sports cars and other performance vehicles.
Disadvantages of Rotary Engines
- Fuel efficiency: Rotary engines are less fuel-efficient than piston engines. This is because they have a larger surface area exposed to combustion, which results in more heat loss.
- Wear and tear: Rotary engines are more prone to wear and tear than piston engines. This is because the rotor and chamber are constantly rubbing against each other, which can cause them to wear out prematurely.
- Emissions: Rotary engines produce more emissions than piston engines. This is because they burn oil to lubricate the rotor, which can lead to increased hydrocarbon emissions.
Conclusion
Rotary engines offer several advantages over piston engines, but they also have some drawbacks. Mazda is the only automaker to have mass-produced cars with rotary engines, but a few other manufacturers have also experimented with them. While rotary engines are no longer in production, they remain a popular choice for enthusiasts and collectors.