Race Car Brake System
Introduction
A race car brake system is a critical component of the vehicle, responsible for slowing down and stopping the car safely and efficiently. Unlike conventional brake systems, race car brake systems are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, high-speed stops, and repeated use without fading or losing performance.
Components of a Race Car Brake System
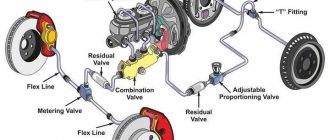
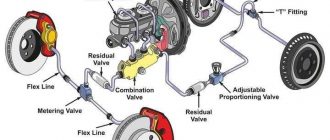
- Brake Pads: Race car brake pads are made of high-friction materials such as carbon fiber or ceramic to provide maximum stopping power. They are designed to withstand high temperatures and repeated use without glazing or fading.
- Brake Rotors: Race car brake rotors are typically made of lightweight and durable materials such as carbon fiber or aluminum alloy. They are designed to dissipate heat quickly and minimize warping under extreme braking conditions.
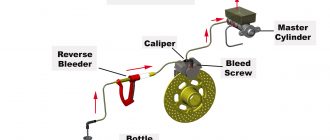
- Brake Calipers: Race car brake calipers are responsible for applying pressure to the brake pads against the rotors. They are typically made of lightweight and rigid materials such as aluminum or titanium.
- Brake Master Cylinder: The brake master cylinder converts the driver’s foot pressure into hydraulic pressure, which is then transmitted to the brake calipers.
- Brake Lines: Brake lines are the hoses that carry brake fluid from the brake master cylinder to the brake calipers. They are made of high-pressure materials to withstand the extreme hydraulic pressure generated during braking.
Types of Race Car Brake Systems
There are several types of race car brake systems, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Disc Brakes: Disc brakes are the most common type of race car brake system. They consist of a brake rotor that rotates with the wheel and brake pads that are mounted on a caliper and press against the rotor.
- Drum Brakes: Drum brakes consist of a brake drum that rotates with the wheel and brake shoes that expand inside the drum to apply friction.
- Calipers: Use of Single fixed 4-piston, 6-piston, or 8-piston caliper, 6-piston being the most common. Used for exceptional braking power, simplicity, and light weight.
- Air Brakes: Air brakes use compressed air instead of hydraulic fluid to apply brake pressure. They are commonly used on heavy-duty vehicles, but they are also found on some race cars.
Design Considerations
When designing a race car brake system, several factors must be considered:
- Stopping Power: The brake system must be able to provide sufficient stopping power to slow down the car quickly and safely.
- Fade Resistance: The brake system must be able to maintain its performance under repeated use without fading or loss of effectiveness.
- Heat Dissipation: The brake system must be able to dissipate heat quickly to prevent overheating and warping.
- Weight: The brake system should be as lightweight as possible to reduce the overall weight of the car.
Maintenance and Inspection
Race car brake systems require regular maintenance and inspection to ensure optimal performance and safety:
- Brake Pad Inspection: Brake pads should be inspected regularly for wear and tear. They should be replaced when they reach the minimum thickness specified by the manufacturer.
- Brake Rotor Inspection: Brake rotors should be inspected for cracks, warping, or other damage. They should be replaced if they are found to be damaged.
- Brake Fluid Inspection: Brake fluid should be replaced regularly according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. It should also be inspected for contamination and leaks.
- Overall Inspection: The entire brake system should be inspected regularly for leaks, loose connections, or other damage. Any issues should be addressed promptly.
Conclusion
A race car brake system is a complex and critical component of the vehicle, responsible for ensuring safe and efficient braking. By understanding the different components, types, design considerations, and maintenance requirements of race car brake systems, race car enthusiasts and professionals can optimize the performance and safety of their race cars.