How is Nitrogen Monoxide Formed in a Car Engine?
Nitrogen monoxide (NO) is a colorless, odorless gas that is a major air pollutant. It is formed when nitrogen and oxygen in the air react at high temperatures. In car engines, NO is formed during the combustion process.
The Combustion Process
The combustion process in a car engine is a complex one, but it can be simplified into three main steps:
- Intake: Air and fuel are drawn into the engine.
- Compression: The air and fuel are compressed by the piston.
- Combustion: The air and fuel are ignited by the spark plug, and they burn rapidly.
During the combustion process, the temperature in the engine can reach up to 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit. At these high temperatures, nitrogen and oxygen in the air react to form NO.
Factors Affecting NO Formation
The amount of NO that is formed in a car engine depends on several factors, including:
- Air-fuel ratio: A lean air-fuel ratio (more air than fuel) produces less NO than a rich air-fuel ratio (more fuel than air).
- Combustion temperature: The higher the combustion temperature, the more NO that is formed.
- Engine design: Some engine designs are more likely to produce NO than others.
Effects of Nitrogen Monoxide
Nitrogen monoxide is a harmful pollutant that can have a number of negative effects on human health and the environment.
Health Effects
Nitrogen monoxide can cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis. It can also contribute to heart disease and cancer.
Environmental Effects
Nitrogen monoxide can contribute to smog and acid rain. It can also damage plants and animals.
Reducing Nitrogen Monoxide Emissions
There are a number of ways to reduce nitrogen monoxide emissions from car engines, including:
- Using cleaner fuels: Fuels that contain less nitrogen, such as natural gas and propane, produce less NO than gasoline.
- Improving engine design: Engine designs that reduce combustion temperatures and promote a lean air-fuel ratio can reduce NO emissions.
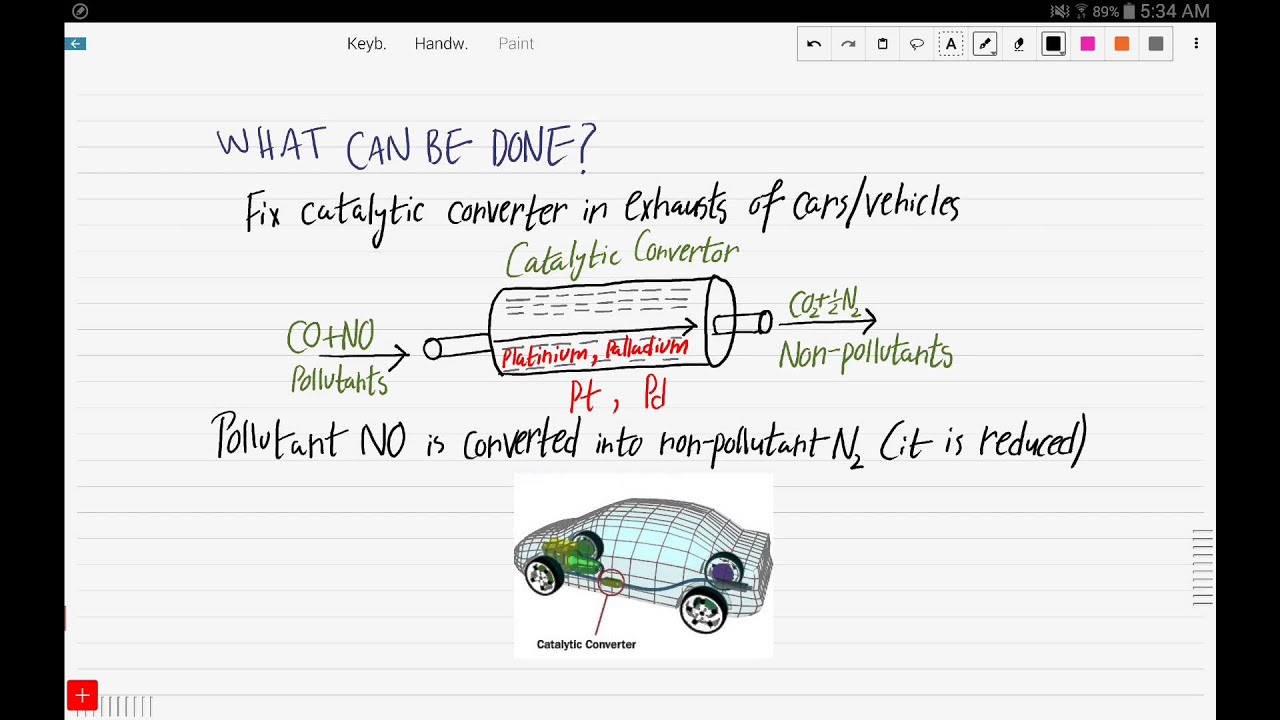
- Using catalytic converters: Catalytic converters are devices that convert NO into less harmful pollutants.
Conclusion
Nitrogen monoxide is a harmful pollutant that is formed in car engines during the combustion process. The amount of NO that is formed depends on a number of factors, including the air-fuel ratio, combustion temperature, and engine design. Nitrogen monoxide can have a number of negative effects on human health and the environment. There are a number of ways to reduce nitrogen monoxide emissions from car engines, including using cleaner fuels, improving engine design, and using catalytic converters.