Understanding the Components and Assembly of a Modern Car Engine
The automobile engine, a marvel of modern engineering, serves as the heart and soul of a vehicle, propelling it forward and providing the necessary power for its operations. The construction of an engine is a complex and intricate process, involving the precision assembly of numerous components. This article delves into the inner workings of a car engine, exploring its key components and the intricate steps involved in its assembly.
The Four Key Components of a Car Engine
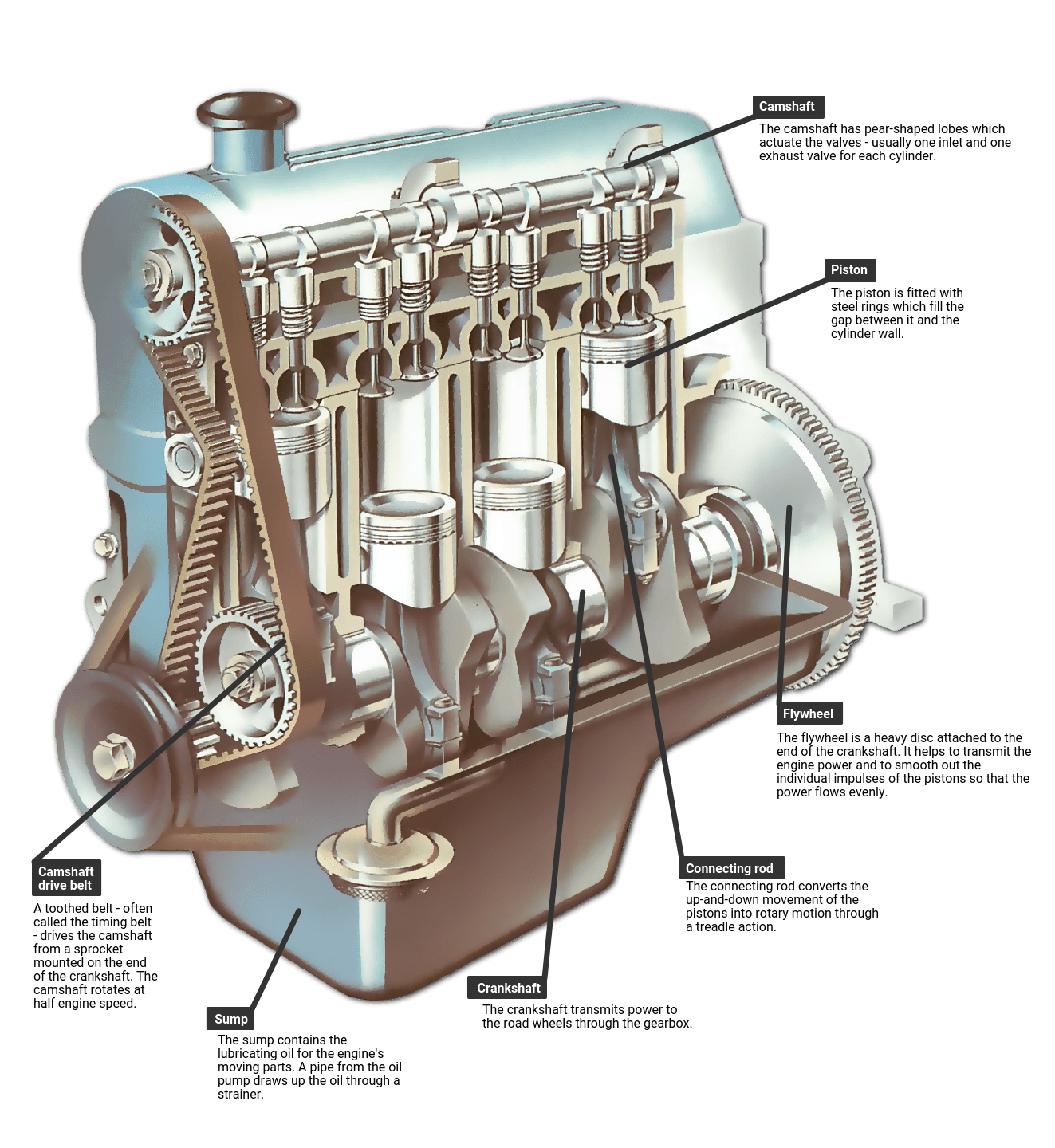
1. **The engine block:** This is the core of the engine, providing structural support and housing the other components. It is typically made of cast iron, aluminum, or a combination of both, and contains the cylinders and coolant passages.
2. **The cylinder head:** This is located at the top of the engine block and forms the combustion chamber. It contains the valves, spark plugs, and camshafts, and is responsible for allowing air and fuel into the cylinders and releasing exhaust gases.
3. **The crankshaft:** This is a rotating shaft located at the bottom of the engine block. It converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion, which is transmitted to the drivetrain.
4. **The pistons:** These are cylindrical components that move up and down within the cylinders. They are responsible for compressing the air and fuel mixture and transmitting the force of the combustion to the crankshaft.
The Assembly Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The assembly of a car engine is a meticulous process that requires precision and attention to detail. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the key steps:
1. **Preparing the engine block:** The engine block is cleaned and inspected for any defects. Cylinder sleeves are installed if necessary, and the crankshaft is placed in position.
2. **Assembling the crankshaft:** The crankshaft is equipped with main bearings, which are lubricated and installed into the engine block. The connecting rods are then attached to the crankshaft.
3. **Installing the pistons:** The pistons are fitted with piston rings and inserted into the cylinders. They are then connected to the connecting rods using piston pins.
4. **Installing the cylinder head:** The cylinder head is placed on top of the engine block and secured with bolts. The intake and exhaust valves are then installed, along with the camshafts.
5. **Installing the camshafts:** The camshafts are positioned above the valves and are responsible for actuating them, allowing air and fuel to enter the cylinders and exhaust gases to escape.
6. **Installing the spark plugs:** The spark plugs are screwed into the cylinder head and provide the electrical spark that ignites the air and fuel mixture.
7. **Connecting the fuel and air system:** The intake manifold is attached to the cylinder head and provides a pathway for air to enter the cylinders. The fuel injectors are also installed at this stage.
8. **Installing the exhaust system:** The exhaust manifold is connected to the cylinder head and collects exhaust gases from the cylinders. These gases are then expelled through the exhaust system.
9. **Connecting the coolant system:** The engine is equipped with a coolant system that regulates engine temperature. This system comprises a water pump, radiator, and hoses.
10. **Connecting the lubrication system:** The lubrication system ensures that all moving parts in the engine are adequately lubricated. This system includes an oil pump, oil filter, and oil passages.
Conclusion
The construction of a car engine is a testament to the ingenuity and precision of modern engineering. The harmonious interplay of its meticulously assembled components allows for the controlled combustion of fuel, generating the power that propels a vehicle forward. Understanding the intricate inner workings of an engine not only enhances our appreciation for this mechanical marvel but also provides valuable insights into its maintenance and performance optimization.