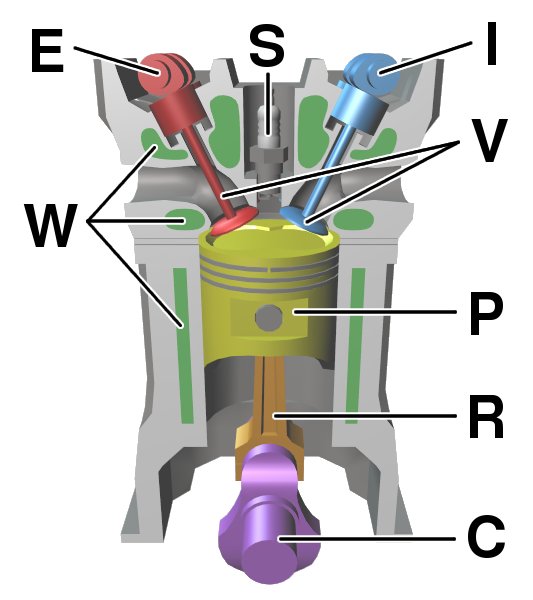
How Does a Car Engine Work?
Introduction
The car engine is a complex machine that converts the chemical energy of gasoline or diesel fuel into mechanical energy
that powers the wheels. It is an internal combustion engine, meaning that the fuel is burned inside the engine itself.
The basic principle of operation is the same for all car engines, regardless of the type of fuel they use.
The Four-Stroke Cycle
The four-stroke cycle is the most common type of engine cycle used in car engines. It consists of four distinct
strokes:
- Intake stroke: The intake valve opens and the piston moves down the cylinder, drawing in a mixture of
air and fuel. - Compression stroke: The intake valve closes and the piston moves up the cylinder, compressing the air-fuel
mixture. This increases its temperature and pressure. - Power stroke: At the top of the compression stroke, a spark plug ignites the air-fuel mixture. This
causes a rapid expansion of the gases, driving the piston down the cylinder. This is the stroke that produces power. - Exhaust stroke: The exhaust valve opens and the piston moves up the cylinder, pushing the exhaust gases out
of the engine. This completes the cycle, and the process repeats itself.
Valve Timing
The timing of the valves is critical to the efficient operation of the engine. The intake valve must open at the
beginning of the intake stroke and close at the end of the compression stroke. The exhaust valve must open at the
beginning of the exhaust stroke and close at the end of the intake stroke.
The timing of the valves is controlled by the camshaft, which is a shaft that runs along the top of the engine. The
camshaft has a series of lobes that open and close the valves. The camshaft is driven by the crankshaft, which is the
main shaft of the engine that converts the power from the pistons into rotational motion.
Fuel Injection
In modern car engines, fuel is injected directly into the cylinders. This is done by a fuel injector, which is a
small device that sprays fuel into the cylinder at high pressure. The fuel injector is controlled by the engine’s
electronic control unit (ECU), which calculates the amount of fuel to inject based on the engine speed and load.
Ignition
The air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug. The spark plug is a small device that creates an electrical spark
between two electrodes. The spark ignites the air-fuel mixture, causing it to burn rapidly.
Power Output
The power output of an engine is measured in horsepower (hp). Horsepower is a measure of the rate at which the engine can
convert fuel into power. The higher the horsepower, the more power the engine can produce.
The power output of an engine is determined by a number of factors, including the engine size, the number of cylinders,
the compression ratio, and the fuel type.
Conclusion
The car engine is a complex and efficient machine that converts the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy that
powers the wheels. The basic principle of operation is the same for all car engines, regardless of the type of fuel
they use.