How Diesel Engine Works in Car
Introduction
Diesel engines are a type of internal combustion engine that uses compression ignition to burn fuel. This means that the fuel is injected into the cylinder and ignited by the heat of compression, rather than by a spark plug. Diesel engines are more efficient than gasoline engines, and they produce less emissions. However, they are also more expensive to manufacture and maintain.
How Diesel Engines Work
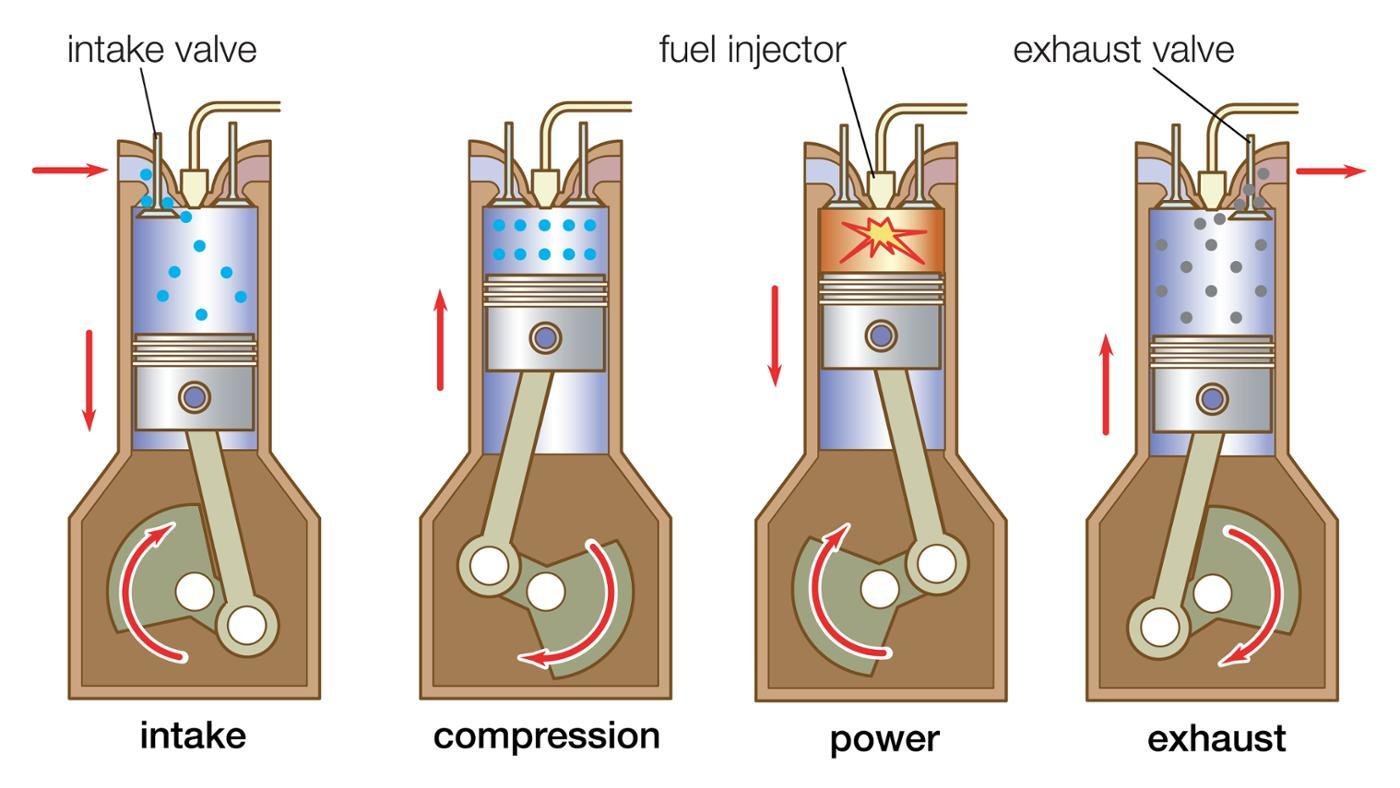
Diesel engines work on a four-stroke cycle. The four strokes are:
- Intake stroke: The piston moves down the cylinder, drawing air into the cylinder.
- Compression stroke: The piston moves up the cylinder, compressing the air.
- Power stroke: The fuel is injected into the cylinder and ignited by the heat of compression. The expanding gases from the combustion drive the piston down the cylinder.
- Exhaust stroke: The piston moves up the cylinder, expelling the exhaust gases from the cylinder.
Diesel Engine Components
The main components of a diesel engine are:
- Cylinder: The cylinder is the space in which the piston moves up and down.
- Piston: The piston is the moving part that compresses the air and fuel in the cylinder.
- Connecting rod: The connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft is the rotating part that converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotary motion.
- Fuel injector: The fuel injector is the device that sprays fuel into the cylinder.
- Turbocharger: The turbocharger is a device that uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which in turn compresses the air going into the cylinder.
Diesel Engine Advantages
Diesel engines have several advantages over gasoline engines, including:
- Higher efficiency: Diesel engines are more efficient than gasoline engines because they burn fuel more completely.
- Lower emissions: Diesel engines produce less emissions than gasoline engines because they burn fuel more efficiently.
- Longer lifespan: Diesel engines typically have a longer lifespan than gasoline engines because they are built more robustly.
Diesel Engine Disadvantages
Diesel engines also have some disadvantages compared to gasoline engines, including:
- Higher cost: Diesel engines are more expensive to manufacture and maintain than gasoline engines.
- Noisier: Diesel engines are typically noisier than gasoline engines.
- Colder starts: Diesel engines can be more difficult to start in cold weather than gasoline engines.
Conclusion
Diesel engines are a powerful and efficient type of engine that is used in a variety of applications, including cars, trucks, and tractors. They offer several advantages over gasoline engines, but they also have some disadvantages. When choosing between a diesel engine and a gasoline engine, it is important to consider your individual needs and preferences.