Diagram of Car Brake System
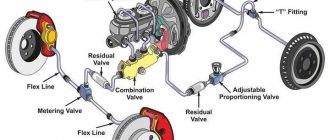
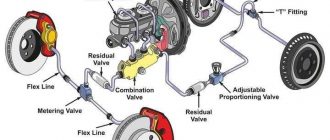
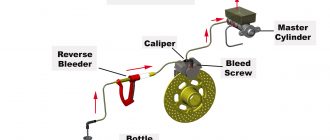
Master Cylinder
The master cylinder is the heart of the brake system. It is responsible for generating the hydraulic pressure that is used to actuate the brakes. The master cylinder is a piston-type pump that is mounted on the firewall of the car. When the brake pedal is depressed, the piston in the master cylinder pushes brake fluid through the brake lines to the calipers or wheel cylinders.
Brake Lines
The brake lines are the pipes that carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers or wheel cylinders. The brake lines are made of steel or copper tubing. They are routed along the chassis of the car and are protected from damage by rubber hoses.
Calipers
The calipers are mounted on the brake rotors. The calipers contain pistons that are actuated by the brake fluid. When the brake pedal is depressed, the pistons in the calipers push the brake pads against the brake rotors. This creates friction that slows down or stops the car.
Wheel Cylinders
Wheel cylinders are used on drum brakes. The wheel cylinders are mounted on the backing plates of the brake drums. The wheel cylinders contain pistons that are actuated by the brake fluid. When the brake pedal is depressed, the pistons in the wheel cylinders push the brake shoes against the brake drums. This creates friction that slows down or stops the car.
Brake Rotors
The brake rotors are mounted on the wheels of the car. The brake rotors are made of cast iron or steel. The brake rotors are smooth and flat on the outside, and they have a series of slots or holes on the inside. When the brake pads are applied to the brake rotors, the friction between the two surfaces slows down or stops the car.
Brake Drums
Brake drums are used on drum brakes. The brake drums are mounted on the wheels of the car. The brake drums are made of cast iron or steel. The brake drums have a smooth and flat surface on the inside, and they have a series of ribs or fins on the outside. When the brake shoes are applied to the brake drums, the friction between the two surfaces slows down or stops the car.
Brake Pads
The brake pads are made of a friction material that is bonded to a metal backing plate. The brake pads are mounted on the calipers. When the brake pedal is depressed, the pistons in the calipers push the brake pads against the brake rotors. This creates friction that slows down or stops the car.
Brake Shoes
The brake shoes are made of a friction material that is bonded to a metal backing plate. The brake shoes are mounted on the backing plates of the brake drums. When the brake pedal is depressed, the pistons in the wheel cylinders push the brake shoes against the brake drums. This creates friction that slows down or stops the car.
Brake Fluid
The brake fluid is a hydraulic fluid that is used to transmit the pressure from the master cylinder to the calipers or wheel cylinders. The brake fluid is made of a glycol base and it содержит additives to prevent corrosion and foaming. The brake fluid is hygroscopic, which means that it absorbs moisture from the air. This moisture can lead to corrosion of the brake system components, so it is important to flush the brake fluid regularly.
Brake Booster
The brake booster is a vacuum-operated device that assists the driver in applying the brakes. The brake booster is mounted on the firewall of the car. When the brake pedal is depressed, the vacuum created by the engine’s intake manifold pulls on a diaphragm in the brake booster. This diaphragm assists the driver in pushing the master cylinder piston and generating hydraulic pressure.
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS)
The ABS is a safety system that prevents the wheels from locking up during braking. The ABS uses a series of sensors to monitor the speed of the wheels. If the ABS detects that a wheel is about to lock up, it modulates the brake pressure to that wheel. This allows the wheel to continue to rotate, which helps to maintain control of the car.
Traction Control System (TCS)
The TCS is a safety system that prevents the wheels from spinning when the car is accelerating. The TCS uses a series of sensors to monitor the speed of the wheels. If the TCS detects that a wheel is spinning, it reduces the engine power or applies the brakes to that wheel. This helps to maintain traction and prevent the car from losing control.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
The ESC is a safety system that helps to prevent the car from skidding. The ESC uses a series of sensors to monitor the car’s speed, steering angle, and yaw rate. If the ESC detects that the car is skidding, it applies the brakes to individual wheels and reduces the engine power. This helps to stabilize the car and prevent it from losing control.