Brake System Problem: Honda Civic Car Won’t Start
Introduction
The brake system is a crucial component of any vehicle, ensuring the safety of both the driver and passengers. However, when problems arise with the brake system, it can lead to various issues, including difficulty starting the car. In this article, we will specifically explore the brake system problem that can cause a Honda Civic car to not start.
Understanding the Brake System
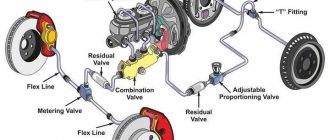
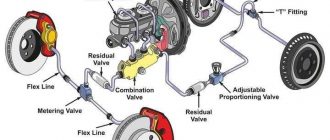
The brake system in a Honda Civic consists of several components that work together to slow down or stop the vehicle. These components include:
- Brake pedal
- Master cylinder
- Brake lines
- Brake calipers
- Brake pads
- Brake rotors
When the brake pedal is pressed, it activates the master cylinder, which pressurizes the brake fluid. The pressurized brake fluid is then distributed through the brake lines to the brake calipers. The calipers squeeze the brake pads against the brake rotors, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle.
Brake System Problem: Brake Light Switch
One common brake system problem that can prevent a Honda Civic from starting is a faulty brake light switch. The brake light switch is a small, electrical switch located near the brake pedal. When the brake pedal is depressed, the switch is activated, sending a signal to the vehicle’s computer. This signal triggers the brake lights to illuminate and also allows the car to start.
If the brake light switch is faulty, it may not send the proper signal to the computer, preventing the car from starting. This problem can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Worn or damaged switch
- Loose or disconnected electrical connections
- Malfunctioning brake pedal assembly
Symptoms of a Faulty Brake Light Switch
There are several symptoms that may indicate a faulty brake light switch:
- Brake lights not illuminating when the brake pedal is pressed
- Car won’t start, even with the brake pedal depressed
- Cruise control not functioning properly
- Check engine light or other warning lights illuminated on the dashboard
Troubleshooting and Repair
If you suspect a faulty brake light switch, it is important to troubleshoot the problem as soon as possible. To troubleshoot the brake light switch, follow these steps:
1. Check the brake lights: With the engine off, press the brake pedal and observe if the brake lights illuminate. If the brake lights do not illuminate, the brake light switch may be faulty.
2. Check the electrical connections: Locate the brake light switch and inspect the electrical connections. Ensure that the connections are secure and free of any corrosion or damage.
3. Test the brake light switch: Using a multimeter, test the brake light switch for continuity. If the switch is faulty, it will not show continuity when the brake pedal is depressed.
If you have determined that the brake light switch is faulty, it should be replaced. Replacing the brake light switch is a relatively simple task that can be performed at home with basic tools.
Other Potential Causes
In some cases, a brake system problem that can cause a Honda Civic car to not start may not be related to the brake light switch. Other potential causes include:
- Low brake fluid level
- Air in the brake lines
- Faulty master cylinder
- Seized brake calipers
- Worn or damaged brake pads or rotors
If you have ruled out the brake light switch as the cause of the problem, it is recommended to consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
Conclusion
A faulty brake system can lead to a variety of issues, including difficulty starting the car. In the case of a Honda Civic, a faulty brake light switch is a common problem that can prevent the car from starting. By understanding the symptoms, troubleshooting the problem, and replacing the faulty switch if necessary, you can ensure that your Honda Civic starts reliably and safely.
It is important to remember that brake system problems can be dangerous if not addressed promptly. If you experience any issues with your vehicle’s brake system, it is crucial to seek professional assistance to avoid any potential safety hazards.