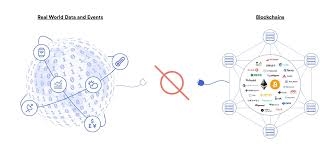
Blockchain oracles are key middlemen that convey data from the actual world to blockchains, which are not connected to the rest of the world. This means that smart contracts can be used in the real world, which is how decentralized finance (DeFi) and other things come about. If oracles didn’t give them trustworthy off-chain information, smart contracts would stay locked in a closed loop. This would mean that they wouldn’t be able to handle the difficulties that they were made to handle in the actual world.
Smart contracts are pieces of code on blockchain ledgers that automatically carry out agreements when certain conditions are satisfied. But in these cases, the data often comes from other places that blockchains can’t get to because they are meant to be distinct from one other to keep things safe and decentralized. This information could be things like checking someone’s identity, tracking a shipment, or getting market prices. This is a paradox: smart contracts need information from outside sources, but they can’t get it on their own. Blockchain oracles make it easy to address this by linking these two areas.
Oracles are like data pipelines that work in real time. They get requests through a contract for an oracle on the blockchain. After then, they use their off-chain portions to ask inquiries, check, and combine data from a number of off-chain sources. They then send the data that has been checked back to the blockchain. This better coordination preserves the blockchain and adds new, correct data.
Experts claim that oracles are needed for ecosystems like DeFi, supply chain management, insurance, gambling, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Price oracles are highly crucial for DeFi systems because they always tell you how much an asset is worth so you can make margin calls and liquidations. Sensors are used by supply chains to set up hardware oracles that keep an eye on shipments. Adding AI-powered analytics to oracles makes them more adaptable and minimizes the chance of employing faulty or corrupted data.
Different kinds of oracles are good for different things:
– **Software Oracles:** You can find information on the internet in databases, APIs, and websites. You have a lot of choices, but you need to be sure that your data can’t be changed.
– **Hardware Oracles:** These connect IoT sensors and other devices in the real world to the blockchain so that they may tell the blockchain what’s going on in the real world.
– **Human Oracles:** People or groups of people who are trusted and agree on something give out complicated or subjective information.
– **Decentralized Oracles:** Independent nodes in a network look at each other’s data to fix the “oracle problem,” which is the fear that centralized data sources could make people lose faith.
Decentralized or hybrid oracle models are the most frequent these days. This means that different nodes collect and check the data. This explanation is very similar to the main ideas behind blockchain, which is that it makes security better and trust less crucial. Chainlink is an excellent example of an extremely reliable oracle network since it uses cryptographic proofs, economic incentives, and confirmation from more than one source.
But adding oracles makes things more difficult. When using oracles, smart contracts need to strike a balance between security, cost, and speed. The *oracle problem* is still a problem because the system’s data isn’t always reliable. This means that the method rewards are given and the way cryptography is tested need to keep getting better.
In the end, oracles help smart contracts see and hear what’s happening in the actual world. They turned blockchain technology from a collection of ledgers into a modern, interactive system. They make peer-to-peer insurance work, trade settlements happen straight away across borders with real market data, game worlds adapt based on what’s going on in the real world, and a lot more. Oracles will become more significant as AI and cryptography get better. They are the main way that smart contracts can work successfully.
Five Important Things to Know About Blockchain Oracles
1. **Bringing Worlds Together:** Oracles take blockchain logic that isn’t the same as the actual world and turn it into data inputs. This means that smart contracts can use information that is happening right now, outside of the blockchain.
2. **Trust and Security:** Decentralized oracles share trust amongst several sources, which makes it much less probable that fraud or downtime will happen. This makes the blockchain trustless.
3. There are many different kinds of oracles utilized in many different areas, such as DeFi, supply chains, insurance, and the Internet of Things.
4. The Oracle Problem: The major problem with decentralization and off-chain data integrity keeps pushing for better cryptographic proofs, consensus mechanisms, and incentive structures.
5. **People who run DeFi and other things:** Oracles give smart contracts data from outside sources that they may trust. This lets blockchain systems turn ideas into powerful motors that help the decentralized economy grow.
We can see how crucial oracles are when we picture of them as a “swarm of bees” that never stops gathering nectar from different flowers (external data sources) and turns it into delicious, reliable honey for smart contracts. They turn blockchains from safe vaults into open, adaptable platforms that can handle all of human activity in a way that makes sense.