## Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) in Cars: A Comprehensive Guide
### Introduction
Anti-lock Brake Systems (ABS) are a crucial safety feature that have become commonplace in modern cars. They play a vital role in preventing wheel lockup during braking, allowing drivers to maintain control and stability even in slippery or emergency situations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the meaning, components, working principles, advantages, and limitations of ABS in cars.
### What is an Anti-Lock Brake System?
An anti-lock brake system is an electronic device that prevents the wheels of a car from locking up when the brakes are applied. This is achieved by rapidly modulating the brake fluid pressure to each wheel, ensuring that the tires maintain contact with the road surface and continue to provide traction.
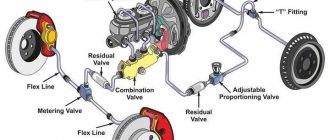
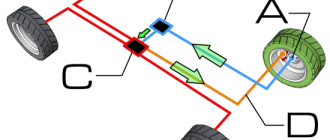
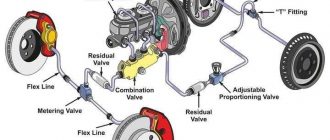
### Components of an ABS System
An ABS system typically consists of the following components:
**1. Wheel Speed Sensors:**
These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel.
**2. Electronic Control Unit (ECU):**
The ECU processes the data from the wheel speed sensors and determines when individual wheels are about to lock up.
**3. Hydraulic Modulator:**
The hydraulic modulator controls the brake fluid pressure to each wheel based on the ECU’s commands.
**4. Brake Lines and Calipers:**
These components apply brake force to the wheels, modulated by the hydraulic modulator.
### How ABS Works
When the ABS system is engaged, it continuously monitors the rotational speed of each wheel. If it detects that a particular wheel is about to lock up (meaning it is slowing down significantly faster than the others), the ECU will reduce the brake fluid pressure to that wheel. This allows the wheel to continue spinning and maintain traction. The process is repeated rapidly, typically several times per second, allowing the tires to regain grip without losing control of the vehicle.
### Advantages of ABS
ABS offers several significant advantages over traditional braking systems:
**1. Improved Vehicle Control:**
By preventing wheel lockup, ABS ensures that drivers maintain control and stability during braking. This is particularly beneficial in slippery conditions such as wet or icy roads.
**2. Shorter Stopping Distances:**
Studies have shown that ABS can reduce stopping distances by up to 25%, especially on low-traction surfaces.
**3. Enhanced Stability:**
ABS helps prevent vehicles from skidding or swerving during braking, improving overall stability and reducing the risk of accidents.
**4. Increased Safety:**
ABS enhances driver safety by providing greater control and reducing stopping distances, making them a crucial safety feature in modern cars.
### Limitations of ABS
While ABS offers numerous benefits, it also has some limitations:
**1. Increased Pedal Pulsation:**
Drivers may feel a pulsing sensation in the brake pedal as the ABS system modulates the brake fluid pressure.
**2. Reduced Effectiveness on Loose Surfaces:**
ABS can be less effective on loose or uneven surfaces such as gravel or snow, as the wheels may lose traction more easily.
**3. Potential for Skidding on Some Surfaces:**
In certain circumstances, ABS can actually cause vehicles to skid on some surfaces, such as ice or packed snow.
### Conclusion
Anti-lock Brake Systems (ABS) are an invaluable safety feature in modern cars. By preventing wheel lockup, ABS enhances vehicle control, reduces stopping distances, improves stability, and increases driver safety. While there are some limitations, ABS plays a crucial role in improving overall driving safety and reducing the risk of accidents. As technology continues to advance, ABS systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, further enhancing their effectiveness and reliability.