Anatomy of Car Brake System
Introduction
The brake system is one of the most important safety features of any car. It allows the driver to control the speed of the vehicle and to stop it safely in an emergency. The brake system is made up of a number of components, each of which plays a vital role in its operation.
Master Cylinder
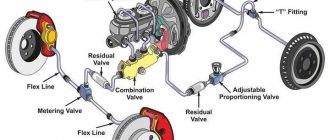
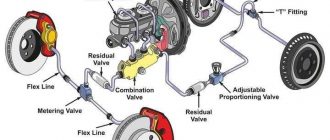
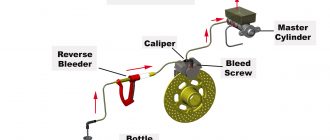
The master cylinder is the heart of the brake system. It is a cylindrical reservoir that stores brake fluid and pressurizes it when the brake pedal is depressed. The master cylinder is connected to the brake pedal by a pushrod.
Brake Lines
The brake lines are a series of tubes that carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers. The brake lines are made of steel or rubber and are routed through the chassis of the vehicle.
Brake Calipers
The brake calipers are mounted on the wheels of the vehicle and contain the brake pads. The brake pads are made of a friction material that grips the brake rotors when the brake pedal is depressed.
Brake Rotors
The brake rotors are mounted on the wheels of the vehicle and provide a surface for the brake pads to grip. The brake rotors are made of cast iron or steel and are designed to dissipate heat.
Brake Shoes
Brake shoes are used in drum brakes and are similar to brake pads. Brake shoes are mounted on the inside of the brake drums and are made of a friction material. When the brake pedal is depressed, the brake shoes expand and contact the inside of the brake drums, slowing the vehicle down.
Brake Drums
Brake drums are used in drum brakes and are similar to brake rotors. Brake drums are mounted on the wheels of the vehicle and provide a surface for the brake shoes to contact. Brake drums are made of cast iron or steel and are designed to dissipate heat.
Brake Booster
The brake booster is a device that assists the driver in applying the brakes. The brake booster is vacuum-operated and is located between the brake pedal and the master cylinder. The brake booster provides additional force to the brake pedal, making it easier for the driver to stop the vehicle.
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
ABS is a system that prevents the wheels of a vehicle from locking up during braking. ABS is a computer-controlled system that uses sensors to monitor the speed of each wheel. If a wheel is about to lock up, ABS will reduce the brake pressure to that wheel, allowing it to continue rotating.
EBD (Electronic Brakeforce Distribution)
EBD is a system that distributes brake force evenly between the front and rear wheels of a vehicle. EBD is a computer-controlled system that uses sensors to monitor the weight distribution of the vehicle. If the weight of the vehicle is shifted to the front or rear, EBD will adjust the brake force to each wheel to ensure that the vehicle stops evenly.
Conclusion
The brake system is a complex and vital part of any car. It is important to understand how the brake system works in order to ensure that it is always in good working order.